87 Sights in Naples, Italy (with Map and Images)
Legend
Premium Sights
Book tickets, guided tours and activities in Naples.
Guided Free Walking Tours
Book free guided walking tours in Naples.
Welcome to your journey through the most beautiful sights in Naples, Italy! Whether you want to discover the city's historical treasures or experience its modern highlights, you'll find everything your heart desires here. Be inspired by our selection and plan your unforgettable adventure in Naples. Dive into the diversity of this fascinating city and discover everything it has to offer.
Sightseeing Tours in NaplesActivities in Naples1. Naples
Naples is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's administrative limits as of 2022. Its province-level municipality is the third-most populous metropolitan city in Italy with a population of 3,115,320 residents, and its metropolitan area stretches beyond the boundaries of the city wall for approximately 30 kilometres. Naples plays also a key international role in international diplomacy, since it is home to NATO's Allied Joint Force Command Naples and of the Parliamentary Assembly of the Mediterranean.
2. Gesù Nuovo
Gesù Nuovo is the name of a church and a square in Naples, Italy. It is located just outside the western boundary of the historic center of the city. To the southeast of the spire, one can see a block away the Fountain of Monteoliveto and the piazza of the church of Sant'Anna dei Lombardi. The square is a result of the expansion of the city to the west beginning in the early 16th century under the rule of Spanish viceroy Pedro Alvarez de Toledo. The square of Gesù Nuovo contains three prominent landmarks:The Church of Gesù Nuovo The Church of Santa Chiara The spire or guglia of the Immaculate Virgin
3. Santa Chiara
Santa Chiara is a religious complex in Naples, Italy, that includes the church of Santa Chiara, a monastery, tombs and an archeological museum. The basilica church of Santa Chiara faces Via Benedetto Croce, which is the easternmost leg of Via Spaccanapoli. The church facade of Santa Chiara is diagonally across from the church of Gesù Nuovo.
4. Teatro di San Carlo
The Real Teatro di San Carlo, as originally named by the Bourbon monarchy but today known simply as the Teatro (di) San Carlo, is a historic opera house in Naples, Italy, connected to the Royal Palace and adjacent to the Piazza del Plebiscito. It is the oldest continuously active venue for opera in the world, having opened in 1737, decades before either Milan's La Scala or Venice's La Fenice.
5. Castle dell'Ovo
Castel dell'Ovo is a seafront castle in Naples, located on the former island of Megaride, now a peninsula, on the Gulf of Naples in Italy. The castle's name comes from a legend about the Roman poet Virgil, who had a reputation in the Middle Ages as a great sorcerer and predictor of the future. In the legend, Virgil put a magical egg into the foundations to support the fortifications. It remains there along with his bones, and had this egg been broken, the castle would have been destroyed and a series of disastrous events for Naples would have followed. The castle is located between the districts of San Ferdinando and Chiaia, facing Mergellina across the sea.
6. Basilica santuario di Santa Maria della Neve
The basilica sanctuary of Santa Maria della Neve is one of the basilicas of Naples. It was the most important church in the municipality of Ponticelli before it became an integral part of the Campania capital.
Wikipedia: Basilica santuario di Santa Maria della Neve (IT)
7. Cathedral of the Assumption of Mary
Naples Cathedral, or the Cathedral of the Assumption of Mary, is a Roman Catholic cathedral, the main church of Naples, southern Italy, and the seat of the Archbishop of Naples. It is widely known as the Cathedral of Saint Januarius, in honour of the city's patron saint.
8. Parco Archeologico del Pausilypon
The archaeological-environmental park of Posillipo or Pausilypon is an archaeological area in the Posillipo district in Naples opened in 2009. Access to the Park for visitors is from the Coroglio 36 descent, through the imposing Grotta di Seiano.
9. Cappella di San Giovanni dei Pappacoda
The Pappacoda Chapel is a monumental chapel in Naples, Italy. it stands in largo San Giovanni Maggiore, adjacent to the basilica of San Giovanni Maggiore and in front of Palazzo Giusso, in the historic center of the city.
10. Amor Divino
The Cappella Sansevero is a chapel located on Via Francesco de Sanctis 19, just northwest of the church of San Domenico Maggiore, in the historic center of Naples, Italy. The chapel is more properly named the Chapel of Santa Maria della Pietà. It contains works of Rococo art by some of the leading Italian artists of the 18th century.
11. Basilica di Santa Maria della Pazienza
The sanctuary of Santa Maria della Pazienza is a complex founded in 1601 and consisting of an ancient hospital and the basilica church of the same name; stands in Naples in Piazza Cesarea, in the Avvocata district, near the Holy Trinity at Caesarea.
12. Basilica di Santa Lucia a Mare
The minor pontifical basilica of the sanctuary of Santa Lucia a Mare is a monumental church in Naples, Italy, which was constituted as a parish and at the same time had the dignity of a sanctuary and, more recently, decreed a minor basilica. The basilica-sanctuary is located in the district of Santa Lucia, within the historic center of Naples. Always a pilgrimage destination, it was erected as a parish in the second half of the 1700s and, in the second half of the 1900s, elevated to a diocesan sanctuary dedicated to the popular cult of Saint Lucia. Administratively, the parish is included in the third deanery of the archdiocese of Naples.
13. San Domenico Soriano
The church of San Domenico Soriano takes its title from the homonymous miraculous image of San Domenico Soriano and is one of the monumental churches of Naples located in Piazza Dante. Here he found burial San Nunzio sulprizio whose body is placed on the high altar and following its canonization in 2018 the church changed its name to the church of the saints Domenico Soriano and Nunzio sulprizio
14. Parco del Forte di Vigliena
The fort of Vigliena is a historic building in the city of Naples, a national monument, of which only a few remains remain today; it is located in the district of San Giovanni a Teduccio, in via Marina dei Gigli.
15. Chiesa della Misericordiella
The church of Santa Maria della Misericordia ai Vergini is one of the churches in Naples, located in the heart of the historic center, on the corner of Via Fuori Porta San Gennaro and Via Misericordiella, right in the entrance area to the Borgo dei Vergini, at Porta San Gennaro. It is part of a complex including the former hospital and the oratory of the Archconfraternity of the Nobles of Santa Maria della Misericordia.
Wikipedia: Chiesa di Santa Maria della Misericordia ai Vergini (IT)
16. Chiesa di Sant'Anna dei Lombardi
Sant'Anna dei Lombardi,, and also known as Santa Maria di Monte Oliveto, is an ancient church and convent located in piazza Monteoliveto in central Naples, Italy. Across Monteoliveto street from the Fountain in the square is the Renaissance palace of Orsini di Gravina.
17. Basilica di San Lorenzo Maggiore
San Lorenzo Maggiore is a church in Naples, Italy. It is located at the precise geographic center of the historic center of the ancient Greek-Roman city, at the intersection of via San Gregorio Armeno and via dei Tribunali. The name "San Lorenzo" may also refer to the new museum now opened on the premises, as well as to the ancient Roman market beneath the church itself, the Macellum of Naples.
18. Parco dell'Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte

The Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte is the Neapolitan department of Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica, the most important Italian institution promoting, developing and conducting scientific research in the fields of astronomy, astrophysics, and space science.
Wikipedia: Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte (EN), Website
19. Chiesa di Sant'Aspreno al Porto
The church of Sant'Aspreno al Porto, also known as the church of Sant'Aspreno ai Tintori, is a place of worship in Naples; the building is located near the port, in Via Sant'Aspreno, incorporated into the side of the Palazzo della Borsa.
20. Chiesa dei Girolamini
The Church and Convent of the Girolamini or Gerolamini is a church and ecclesiastical complex in Naples, Italy. It is located directly across from the Cathedral of Naples on via Duomo. The facade is across the homonymous piazza and street from Santa Maria della Colonna. It is one block west of Via Duomo.
21. San Pietro a Majella
San Pietro a Majella is a church in Naples, Italy. The term may also refer to the adjacent Naples music conservatory, which occupies the premises of the monastery that used to form a single complex with the church.
22. Catacombe di San Gennaro
The Catacombs of San Gennaro are underground paleo-Christian burial and worship sites in Naples, Italy, carved out of tuff, a porous stone. They are situated in the northern part of the city, on the slope leading up to Capodimonte, consisting of two levels, San Gennaro Superiore, and San Gennaro Inferiore. The catacombs lie under the Rione Sanità neighborhood of Naples, sometimes called the "Valley of the Dead". The site is now easily identified by the large church of Madre del Buon Consiglio.
23. Chiesa di Santa Maria del Divino Amore
The church of Santa Maria del Divino Amore is a monumental church in the city of Naples, located between Piazzetta del Divino Amore, Via del Grande Archivio, Via de Blasiis and Vicoletto Paparelle al Pendino.
24. Basilica di San Paolo Maggiore

San Paolo Maggiore is a basilica church in Naples, southern Italy, and the burial place of Saint Cajetan, founder of the Theatines. It is located on Piazza Gaetano, about 1-2 blocks north of Via dei Tribunali.
25. Chiesa di San Giovanni a Carbonara
San Giovanni a Carbonara is a Gothic church in Naples, Southern Italy. It is located at the northern end of via Carbonara, just outside what used to be the eastern wall of the old city. The name carbonara was given to this site allocated for the collection and burning of refuse outside the city walls in the Middle Ages.
26. Galleria Umberto I
Galleria Umberto I is a public shopping gallery in Naples, southern Italy. It is located directly across from the San Carlo opera house. It was built between 1887 and 1890, and was the cornerstone in the decades-long rebuilding of Naples—called the risanamento —that lasted until World War I. It was designed in the Stile Umbertino by Emanuele Rocco, who employed modern architectural elements reminiscent of the Galleria Vittorio Emanuele II in Milan. The Galleria was named after Umberto I, King of Italy at the time of construction. It was meant to combine businesses, shops, cafés and social life—public space—with private space in the apartments on the third floor.
27. Chiesa dei Santi Alberto e Teresa
The church of Saints Joseph and Christopher, also known as the church of Saints Albert and Teresa, is a Catholic place of worship of historical and artistic interest in the historic center of Naples, located in Piazza Santa Maria la Nova.
28. Chiesa di San Gregorio Armeno
San Gregorio Armeno is a church and a monastery in Naples, Italy. It is one of the most important Baroque complexes in Naples. The church is located on a street of the same name just south of Via dei Tribunali and a few blocks south of the church of San Paolo Maggiore, Naples
29. Cimitero delle Fontanelle
The Fontanelle cemetery in Naples is a charnel house, an ossuary, located in a cave in the tuff hillside in the Materdei section of the city. It is associated with a chapter in the folklore of the city. By the time the Spanish moved into the city in the early 16th century, there was already concern over where to locate cemeteries, and moves had been taken to locate graves outside of the city walls. Many Neapolitans, however, insisted on being interred in their local churches. To make space in the churches for the newly interred, undertakers started removing earlier remains outside the city to the cave, the future Fontanelle cemetery. The remains were interred shallowly and then joined in 1656 by thousands of anonymous corpses, victims of the great plague of that year.
30. Chiesa dei Santi Bernardo e Margherita
The Church of Saints Bernardo and Margherita is a monumental church in Naples, Italy. The building is incorporated into the Sovereign Military Order of Malta Complex, and is also known as the Sovereign Order of Malta's St. John's Church.
31. Santa Caterina a Formiello
Santa Caterina a Formiello is a church in Naples, in southern Italy, located at the extreme eastern end of the old historic center of the city, on Via Carbonara and Piazza Enrico de Nicola, near the gate called Porta Capuana. The term Formiello comes from the forms or containers for water spouts found in the convent. Diagonally across the street and South is the Fontana del Formiello against the rear wall of the imposing Castel Capuano.
32. Chiesa delle Crocelle ai Mannesi
The church of San Francesco d'Assisi, popularly known as the church of the Crocelle ai Mannesi, is a building of historical and artistic interest in Naples; It is located in the heart of the historic center, in the square of the same name.
33. Santa Caterina della Spina Corona
The church of Santa Caterina della Spina Corona is a monumental church in Naples, Italy. On one of the external walls of the building rests the Fountain of the Spinacorona, locally known as the Zizze.
34. Basilica di San Gennaro fuori le mura
San Gennaro extra Moenia is a church in Naples, Italy. It is located in the Rione Sanita on the large road that leads up to the Capodimonte museum and is an example of so-called paleo-Christian architecture in the city.
35. Santa Maria del Rifugio
The church of Santa Maria del Rifugio is a building used for Catholic worship located in the San Lorenzo district in Via Tribunali, in Naples; it is just a few meters from the churches of Santa Maria della Pace and San Tommaso a Capuana.
36. Gallerie d'Italia

Gallerie d'Italia is the museum center owned by Intesa Sanpaolo, set up to make its artistic and architectural heritage usable, like the collections from the Cariplo Foundation in Milan, another partner in the project. They are based in Naples, Milan, Turin and Vicenza. The director of the Gallerie d'Italia is Michele Coppola, Executive Director of Art, Culture and Historical Heritage of Intesa Sanpaolo.
37. Chiesa dei Santi Pietro e Paolo dei Greci
Santi Pietro e Paolo dei Greci is a church at the Campania, the historic center of Naples, in Via San Tommaso d'Aquino 51. It was the center of the Scuola dei Greci in Naples and the Confraternity of the Greeks in Naples. Around this period there was a similar church in Venice called San Giorgio dei Greci. There was also a Greek Brotherhood of Venice. A prominent member of the Greek Brotherhood was famous painter Belisario Corenzio. The church was initially dedicated to the Twelve Apostles. They began building the church at the request of one of the descendants of the Byzantine Empire Thomas Asen Palaiologos. The church currently belongs to the Greek State.
38. Chiesa di Santa Patrizia
The church of Santa Patrizia is an ancient church in Naples; it is located in via Armanni. The complex actually has an additional place of worship of historical and artistic interest so called; it, in order not to be confused with this one in question, is often called the internal Saint Patrician.
39. Museo del Corallo Ascione
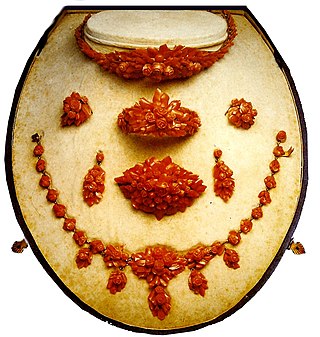
The Museo del Corallo is a small private museum of coral jewellery in Naples, in Campania in southern Italy. It also holds some cameos and jewellery in ivory and tortoiseshell. The works date from 1805 to 1950.
40. Basilica dell'Incoronata Madre del Buon Consiglio
The Madre del Buon Consiglio is a Roman Catholic church in Naples, southern Italy. It is located on the hillside leading up to the Capodimonte palace and art museum and is visible from many quarters of the city. The church houses a number of works of art rescued from closed, damaged, or abandoned houses of worship in the city. It was building from 1920 to 1960.
41. Chiesa di Santa Maria di Costantinopoli
The Church of Santa Maria di Costantinopoli is a 16th-century Roman Catholic church located on the street of the same name in Naples, Italy, and located a block north of the Academy of Fine Arts of Naples.
42. Chiesa di Santa Teresella degli Spagnoli
The church of Santa Teresella degli Spagnoli is one of the churches of historical and artistic interest in Naples closed to worship; it is located in the street of the same name, in the Spanish Quarters. The
43. Chiesa della Pietà dei Turchini
The Church of Pietà dei Turchini is a religious building in Naples, Italy. A smaller church, located on Rua Catalana, was built originally in 1592–1595 by the Confraternity of the Incoronatella. This church was nearly destroyed by an explosion in the Castel Nuovo in 1638. It was rebuilt in 1638–1639, and retitled Santa Maria Incoronatella della Pietà dei Turchini when it acquired a dome. The facade was completed in 1769–70 by Bartolomeo Vecchione.
44. Basilica di Santa Maria della Sanità
The Basilica of Santa Maria della Sanità is a basilica church located over the Catacombs of San Gaudioso, on a Piazza near where Via Sanità meets Via Teresa degli Scalzi, in the Rione of the Sanità, in Naples, Italy. The church is also called San Vincenzo or San Vincenzo della Sanità, due to the cult of an icon of San Vincenzo Ferrer, also called locally O' Monacone.
45. Chiesa di Sant'Angelo a Nilo
Sant'Angelo a Nilo is a Roman Catholic church located on the Decumano Inferiore in Naples, Italy. It stands diagonally across from San Domenico Maggiore in Naples. It is known for containing the monumental Renaissance-style tomb of Cardinal Rainaldo Brancacci by Donatello and Michelozzo, one of the major sculptural works in the city.
46. Chiesa di San Nicola a Pistaso

The church of San Nicola a Pistaso is a place of worship of historical and artistic interest in Naples, located in via San Biagio dei Librari, the toponym in Pistaso refers to the homonymous minor seat of the Sedile di Forcella present in that area of the city.
47. Botanical Garden of Naples
The Botanical Garden of the University of Naples Federico II is a research facility and botanical garden of the University of Naples Federico II. The premises take up about 15 hectares and are located in via Foria, adjacent to the historical edifice Albergo dei Poveri, the Royal Hospice for the Poor under the Bourbon dynasty. The facility is part of the university's Department of Natural Science. It is one of Naples's many scientific and educational facilities established under French rule (1806–15). The garden opened in 1810.
Wikipedia: Botanical Garden of the University of Naples Federico II (EN)
48. Chiesa di Sant'Eligio Maggiore
Sant’Eligio Maggiore is a church in Naples, southern Italy. It is located near Piazza Mercato, and was built during the reign of Charles of Anjou by the same congregation that built the nearby Sant’Eligio hospital in 1270. It is the first church built in Naples by the Angevin dynasty and therefore the first one in Gotico Angioiano style.
49. Chiesa Cor Jesu
The church Cor Jesu, also known as the church of the Santissimo Cuore di Gesù or the church of Jesus in the garden of olives, is a church in Naples located in via Amato di Montecassino, in the area of San Raffaele, in Materdei, between the church of the Conception in Materdei and the church of San Raffaele.
50. Basilica di Santa Restituta
Santa Restituta is a church in Naples, southern Italy, dedicated to Saint Restituta. The foundation of the basilica is attributed to the Emperor Constantine the Great in the 4th century and is mentioned in a passage from the life of Pope Sylvester I in the Liber pontificalis:
51. Torre La Brava
The Carmine Castle was a castle in Naples, Italy. It was one of the fortifications built by the Spaniards under viceroy Pedro Álvarez de Toledo in the mid-16th century as part of the Spanish plans to surround the city with walls and forts. It stood at what was then the south-east corner of the walled city, that wall then turning in to the north. The fortress had great strategic value in the military history of the city up to and including the defense of the Neapolitan Republic of 1799 against the returning royalist forces of King Ferdinand IV. The castle was partially demolished in 1900 as part of Naples' great urban renewal in order to make room for a road along the sea. Two towers and fragmentary ruins still stand as historic markers.
52. Chiesa di Santa Maria Egiziaca a Forcella
Santa Maria Egiziaca a Forcella, also known as the Church of Santa Maria Egiziaca all'Olmo, is a Baroque-style, Roman Catholic church located in the quartiere di Forcella, in the city of Naples, Italy.
53. Fontana del Nettuno
The Fountain of Neptune is a monumental fountain, located in Municipio square, in Naples, Italy. The fountain until the end of 2014 was located across the street of via Medina across from the church of Santa Maria Incoronata, Naples and a few doors south of the church complex of Pieta di Turchini. Now the fountain is located in front of the Town hill building, its location changed due to the construction of the new underground station.
54. Villa Comunale
The Villa Comunale is a park in Naples, Southern Italy. It was built in the 1780s by King Ferdinand IV on land reclaimed along the coast between the main body of the city and the small port of Mergellina. The park was originally a "Royal Garden", reserved for members of the royal family, but open to the public on special holidays such as the Festival of Piedigrotta. The park was opened to the general public on a permanent basis in 1869 after the unification of Italy.
55. Santa Maria della Pace
Santa Maria della Pace is a Roman Catholic church attached to a monastery and hospital, located on Via dei Tribunali corner with Via Castel Capuano, just after the piazzetta Sedil Capuano, in Naples, Italy.
56. Chiesa dei Santi Crispino e Crispiniano
The church of Saints Crispino and Crispiniano, also known as the church of the shoemakers, is a church in Naples, located in Via Antonio Ranieri, in the Duchesca area. Founded in the first half of the sixteenth century, it contains some paintings by local authors.
57. Chiesa di San Diego all'Ospedaletto
San Diego all'Ospedaletto, also known as San Giuseppe Maggiore, is a Baroque-style church located on via Medina in the rione Carità in Naples, Italy. It is located across the street from the tall modern NH Ambassador Hotel and diagonal from the Palazzo Giordano and Questura.
58. Chiesa del Gesù delle Monache
Gesù delle Monache is a Roman Catholic church located near the Porta San Gennaro in central Naples, Italy. Over the years, the church was also a parish church known as San Giovanni Evangelista in Porta San Gennaro or San Giovanni in Porta.
59. Chiesa di San Carlo all'Arena
San Carlo all'Arena is a Roman Catholic church built in a Baroque-style layout with a Neoclassic façade, and located on via Foria in the quartiere or neighborhood of the San Carlo all'Arena, in the city of Naples, Italy.
60. Chiesa dell'Ecce Homo ai Banchi Nuovi
The church of the Ecce Homo ai Banchi Nuovi is a church in Naples located in Piazzetta Ecce Homo, near the churches of Saints Cosma and Damiano ai Banchi Nuovi and Santa Maria dell'Aiuto. It is so called to distinguish it from the Church of the Ecce Homo in Cerriglio.
61. Chiesa di Santa Caterina a Chiaia
Santa Caterina a Chiaia is a Roman Catholic church located on via Santa Caterina 76 in Naples, Italy. It is located near Piazza dei Martiri in the Chiaia section of the city, near where Via Santa Caterina flows toward the tree-shaded Via Chiaia.
62. Teatro Mediterraneo
The Mediterranean Theater, then Mediterranean Theater and Auditorium, is a Neapolitan theater. Inaugurated in 1940, it is part of the majestic complex of the Mostra d'Oltremare, in the Fuorigrotta district of Naples.
63. Chiesa di San Giacomo degli Spagnoli
San Giacomo degli Spagnoli is a basilica church in Piazza Municipio in central Naples, Italy. The Renaissance church was enveloped in 1812 by the Palazzo San Giacomo built by King Ferdinand I of Bourbon when he built a central block of offices for the ministries of his government adjacent to the fortress of the Castel Nuovo. The Palazzo San Giacomo is now the municipio or city hall of Naples. Another church of San Giacomo degli Spagnoli is found in Rome.
64. San Biagio Maggiore
The church of San Biagio Maggiore also known to its locals as 'Santa Patrizia' is a small former religious edifice located at the intersection of Via San Biagio dei Librai and Via San Gregorio Armeno, which was an integral part in the city center of Naples, Italy. It is adjacent, and for many years integral to the church of San Gennaro all’Olmo.
65. Chiesa di San Giorgio dei Genovesi
San Giorgio dei Genovesi is a church on Via Medina in the Center of Naples, Italy. It is adjacent and just north of the Church of the Santa Maria Incoronata, two doors south from the Palazzo d’Aquino di Caramanico, and across the street from the Church of the Pietà dei Turchini.
66. Fontana di Capodimonte
The Capodimonte fountain is one of the historic fountains of Capodimonte (Naples); located at the Tondo di Capodimonte, in the immediate vicinity there is the basilica of the Incoronata Madre del Buon Consiglio and the monumental fountain of the Duchess.
67. Chiesa di Santa Barbara dei Marinai
The church of Saint Barbara of the Gunners or Santa Barbara dei Cannonieri e dei Marinai is a small religious edifice in central Naples, Italy. It is located on Rua Catalana, near the church of San Giacomo degli Italiani. The church embedded in the Castel Nuovo of Naples, has also been called Santa Barbara.
68. Chiesa di Santa Caterina da Siena
The church of Santa Caterina da Siena is located in the city center of Naples, Italy, and while built in the 16th century, the interior was decorated by Baroque era artists over the next two centuries.
69. Fontana del Formello
The Fontana del Formiello is a historic public fountain located at the rear exterior of the Castel Capuano, facing Piazza Enrico de Nicola, and across the street from the church and convent of Santa Caterina a Formiello in Naples, Italy. The term Formiello comes from the forms or containers for water spouts found in the convent. The fountain had been placed in storage during the late 19th century, and reconstructed at this site in 1930.
70. Obelisco di Portosalvo
The Portosalvo Obelisk is an obelisk in Naples, located in Via Alcide De Gasperi, next to the church of Santa Maria di Portosalvo. It is one of the last obelisks to have been erected in chronological order in the city.
71. Santa Maria della Graziella
The church of the Graziella al Porto Napoli or Santa Maria delle Grazie al Porto Napoli is a small Roman Catholic church in Naples, Italy. The church is just behind the church of Pietà dei Turchini, on vico Graziella al Porto. It is accessible through narrow alleys from via Medina, along the church of San Diego all'Ospedaletto and the former Royal Conservatory, but also by pedestrian alleys from via Guglielmo San Felice and via De Pretis. It is located in the rione San Giuseppe Carità.
72. Gesù Vecchio dell'Immacolata di Don Placido
The Gesù Vecchio is a church in Naples, Italy. Its full title is the Basilica Sanctuary of the Gesù Vecchio or Basilica Sanctuary of the Immaculate Conception and Don Placido. It was founded in 1554 and promoted to minor basilica status in 1958. Its name distinguishes it from the nearby Gesù Nuovo, built to cope with the expansion of the Jesuit order in the city.
73. Chiesa di San Giorgio Maggiore
San Giorgio Maggiore is a basilica church located on the corner of Via vicaria Vecchia and Via Duomo, in central Naples, Italy. The apse of the church lies diagonally across the street from San Severo al Pendino.
74. Mausoleo Schilizzi
The Mausoleo Schilizzi, also known as the Mausoleum of Posillipo or Ara Votiva per i Caduti della Patria is a monumental mausoleum built in the 1880s in a Neo-Egyptian style. It is located at Posillipo, Naples, and overlooks the bay from atop a hillside.
75. Chiesa di Santa Maria ad Ogni Bene dei Sette Dolori
Santa Maria ad Ogni Bene dei Sette Dolori, also known as Santa Maria de Sette Dolori, is a Roman Catholic church in Naples, Italy. It stands on a hill, providing an excellent view of Spaccanapoli, a Decumanus of Naples which ends across via Francesco Girardi. From the door of the church, one has a direct view across Naples through the straight decumanus. The church also faces the former convent of Santissima Trinità delle Monache.
76. Chiesa dei Santi Marco e Andrea a Nilo
The church of Santi Marco e Andrea a Nilo is a former Roman Catholic church, located on via Paladino #50 in central Naples, Italy. It is less than a block east of the Santa Maria Assunta dei Pignatelli church.
77. Chiesa di Santa Maria Egiziaca a Pizzofalcone
Santa Maria Egiziaca a Pizzofalcone is a Baroque-style, Roman Catholic, Basilica church on the street of the titular name in the hill of Pizzofalcone, in the historic center of Naples, region of Campania, Italy. The church layout was initially designed by Cosimo Fanzago.
78. Chiesa di Santa Maria di Portosalvo
Santa Maria di Portosalvo or Santa Maria fuori le mura is a former Roman Catholic church in Naples, Italy. It is situated on via Alcide De Gasperi, at the start of via Marina, near the harbour and outside the city walls.
79. Chiesa di Santa Maria Maddalena de' Pazzi
Santa Maria Maddalena de’ Pazzi, also known as the church dei Pazzi or dei Pazzi del Santissimo Sacramento, is a Roman Catholic church in central Naples, Italy; its baroque facade opens on via Salvator Rosa, near vico Nocelle.
80. Chiesa di Sant'Agrippino a Forcella
Sant'Agrippino a Forcella is a church located on Via Forcella in Naples, Italy. A church at the site may have been present since the fifth century, but we have documentation of a consecration during the papacy of pope Clement IV in 1265-1268.
81. Chiesa dei Santi Cosma e Damiano ai Banchi Nuovi
Santi Cosma e Damiano ai Banchi Nuovi is a deconsecrated church dedicated to Cosmas and Damian in Naples. It is sited on largo Banchi Nuovi and owes its name to the Banchi Nuovi, whose loggia previously occupied the church's site. The church was founded in 1616 and re-used the loggia's facade. It was extended later in the 17th century, including a scheme led by the engineer Luigi Giura. Its high altarpiece is now in the Diocesan Museum.
82. Chiesa di Gesù e Maria
Gesù e Maria Complex was a small monastic complex in Naples which also included the monastic church. The monastery buildings now house a hospital. It is sited on the summit of the zona di Pontecorvo. It was first built for the Dominican friar Silvio d'Atripalda in 1580 - he had obtained its site from Ascanio Coppola. In 1585 the complex was remodelled and extended in the Baroque style by Domenico Fontana - it is one of his earliest works. The Dominicans were expelled in 1812 and their lands and buildings confiscated by the French occupiers. It had passed to another order by 1863, when the monastic buildings were again secularised and turned into a hospital but the church retained as a parish church. It was already in a state of decay by the end of the 19th century and so in 1979 the church was closed, after which it was hit by thefts, the 1980 earthquake and looting. The hospital had been demolished in the meantime. The church was briefly opened for a month in 2012 but it has not yet been fully restored and its future is uncertain.
83. Collina dei Camaldoli
The Camaldoli hill is the highest point in the city of Naples, with a maximum altitude of 457 meters above sea level. It extends between the municipality of Naples and the municipalities of Marano di Napoli and Quarto. The hill is estimated to be about 35,000 years old and to have formed from violent volcanic eruptions in the Phlegraean Fields.
84. Cappella Pontano
The Pontano Chapel is a small Renaissance temple in Naples located in the ancient center of the city, along the major decumanus, between Via del Sole and Via dei Tribunali. The building also houses the church of Santa Maria Maggiore alla Pietrasanta.
85. Chiesa di Santa Luciella a San Biagio dei Librai
The Church of Santa Luciella ai Librai is one of the churches in the historic center of Naples; it is located in the street of the same name, near the church of Saints Philip and James and behind the church of San Gregorio Armeno.
Wikipedia: Chiesa di Santa Luciella a San Biagio dei Librai (IT)
86. Basilica Pontificia di San Gennaro ad Antignano
The Pontifical Minor Basilica of San Gennaro in Antignano is one of the monumental churches of Naples. it stands in the V Municipality of Arenella-Vomero, in the Vomero District, in via San Gennaro in Antignano nº 82.
87. Guglia di San Gennaro
The obelisk of San Gennaro is a Baroque obelisk dating back to between 1636 and 1660 designed in marble and bronze by Cosimo Fanzago and located in Piazza Riario Sforza in Naples, between the royal chapel of the Treasure of San Gennaro and the Pio Monte della Misericordia.
Share
Disclaimer Please be aware of your surroundings and do not enter private property. We are not liable for any damages that occur during the tours.

















































































