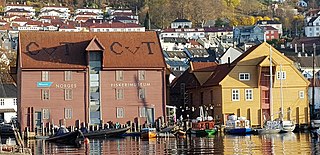43 Sights in Bergen, Norway (with Map and Images)
Legend
Premium Sights
Book tickets, guided tours and activities in Bergen.
Guided Free Walking Tours
Book free guided walking tours in Bergen.
Welcome to your journey through the most beautiful sights in Bergen, Norway! Whether you want to discover the city's historical treasures or experience its modern highlights, you'll find everything your heart desires here. Be inspired by our selection and plan your unforgettable adventure in Bergen. Dive into the diversity of this fascinating city and discover everything it has to offer.
Sightseeing Tours in BergenActivities in BergenSandviksfjellet is a mountain in the city of Bergen in Vestland county, Norway. It is one of the traditional seven mountains that surround the city centre of Bergen. The mountain lies on the east side of the city neighborhood of Sandviken, just north of the mountain Fløyen. The European route E39 highway runs through the mountain as part of the Fløyfjell Tunnel.
Bryggen, also known as Tyskebryggen, is a series of Hanseatic heritage commercial buildings lining up the eastern side of the Vågen harbour in the city of Bergen, Norway. Bryggen has been on the UNESCO list for World Cultural Heritage sites since 1979.
St Mary's Church is a parish church of the Church of Norway in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located in the Bryggen area in the central part of the city of Bergen. It is one of the churches for the Bergen Cathedral parish which is part of the Bergen domprosti (arch-deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The large, gray stone church was built in a long church design using plans drawn up by an unknown architect. The church seats about 240 people. The construction of the church is believed to have started in the 1130s or 1140s and completed around 1180, making this church the oldest remaining building in the whole city of Bergen. There have been a few fires that burned the church, as well as several renovations and reconstructions, most recently in 2013.
4. Fløibanen, nedre stasjon;Fløibanen
The Fløibanen is a funicular railway, owned by Fløibanen AS, in the Norwegian city of Bergen. It connects the city centre with the mountain of Fløyen, with its mountain walks and magnificent views of the city. It is one of Bergen's major tourist attractions and one of Norway's most visited attractions. The line is 848 m (2,782 ft) long, covers a height difference of 302 m (991 ft), and carries nearly two million passengers a year.
5. VilVite
VilVite is a science centre at Møhlenpris in one of Mjellem & Karlsen Verft's former workshop halls. The Science Centre was previously located at Bergen University College, but moved to new premises in 2007. The centre opened here on 31 May 2007.
6. Bergen Leprosy Museum
The Leprosy Museum, also called St. Jørgen's Hospital, is located in Marken in the center of Bergen, and is currently run by the City Museum in Bergen. In recent years, the museum has been the subject of increasing attention, and in recent years has been nominated for several national and international awards.
7. Hagerupgården
Hagerupgården or Stiftsgården is located at Rådstuplass 9 in Bergen. The building is a baroque mansion designed after the city fire on May 19, 1702. The building is attributed to architect Johan Conrad Ernst and the house's drawings were submitted to the zoning commission before 20 May 1703, the year after the city fire. Master mason Hans Martin Heintz was the master builder for the construction of the farm in 1704–1705. Responsible for the sandstone detailing were three Italian stonemasons named Giovanni Maria Fontana, Charles Fera and Gallas Qvadrat.
8. Bergen domkirke
Bergen Cathedral is a cathedral in the city of Bergen in Vestland county, Norway. It is the episcopal seat of the Diocese of Bjørgvin as well as the seat of the "Bergen domkirke" parish and the seat of the Bergen domprosti (arch-deanery). It is part of the Church of Norway. The first recorded historical reference to this church is dated 1181. It retains its ancient dedication to Saint Olaf. The cathedral seats about 600 people.
9. Old Bergen

The Old Bergen Museum is an open-air museum located in the district of Ytre Sandviken. It is built around the old pleasure place Elsesro. The museum was opened in 1949 and is now part of the Bergen City Museum. The open-air museum has buildings from the 1700s and 1800s that have been moved from different areas of Bergen to this area. The building stock consists mainly of one- and two-storey log houses with cladding, and tiled roofs.
10. Kjøttbasaren
The meat bazaar is located in Vetrlidsallmenningen 2 in Bergen. The city's bazaar, as the building was originally called, was designed by city conductor and architect Conrad Fredrik von der Lippe, and built in 1874–1876 in neo-Romanesque style. Art historian Per Jahn Lavik calls the style "Florentine Neo-Renaissance". von der Lippe also designed two important flank buildings for the Meat Bazaar, Vetrlidsalmenningen 1 and the brick bag for the Hanseatic Museum. The meat bazaar was built to control the market trade and the sale of food products, with a view to fraud and hygiene.
11. Motehuset Sundt
Sundt's department store is located at Torgallmenningen 14 in the center of Bergen. The building was designed by the architect Per Grieg, and the department store opened on 18 July 1938. 50 years later, in 1988, the building was protected, as a result of the cultural monument being threatened by extensions at height. What has been preserved of the original interior is also included in the preservation. Sundt department store is considered one of the main works of functionalism in Norway. In 1961, the architect was awarded the Houen Foundation's diploma for the building. The building is currently owned by DNB Næringseiendom AS. In the period 2022-24, the entire building will be rehabilitated, due to rust damage to the rebar. The building is completely closed while the repairs are ongoing.
12. St. John's Church
St. John's Church is a parish church of the Church of Norway in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located in the Sydnes area of the city of Bergen. It is one of the five churches for the Bergen Cathedral parish which is part of the Bergen domprosti (arch-deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The red brick church was built in a cruciform design between 1891 and 1894 in the Gothic Revival style. The architect was Herman Backer. The church seats 690 people, making it the largest church in Bergen. It was consecrated on 15 March 1894.
13. Forum Scene

Forum cinema is a former cinema building at Danmarks plass, Fjøsangerveien 28 in Bergen. The building was designed by Ole Landmark in 1936 and was completed in 1946. It was the largest cinema in Bergen until it was closed down in 2005.
14. Korskirken
Holy Cross Church is a special parish church in Bergen municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is situated in the centre of the city of Bergen, just east of the head of the Vågen bay. The church is located at the intersection of the streets Kong Oscars gate and Nedre Korskirkeallmenningen. It is one of the churches for the Bergen domprosti parish which is part of the Bergen domprosti (arch-deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The large stone church was built in a cruciform design around the year 1150 using plans drawn up by an unknown architect. The church seats about 600 people.
15. Maritime Museum

The Bergen Maritime Museum was founded on 13 April 1921 and had its official opening on 18 February 1927. In 1962, the museum moved into its own building designed by architect Per Grieg. It has a monumental Romanesque style with strong stone walls. The exhibition rooms are built around an inner atrium with glass walls that help to make them bright and pleasant. The exhibitions cover the entire history of seafaring from the earliest times to the present day. There are several unique objects and an extensive collection of models of famous vessels. The museum is also used as a banquet room.
16. Løvstakken
Løvstakken is one of the Seven Mountains that surround the center of the city of Bergen in Vestland county, Norway. The 477-metre (1,565 ft) tall mountain is located between the Fyllingsdalen and Bergensdalen valleys on the Bergen Peninsula. Løvstakken and the forests nearby are popular hiking areas among the locals since it is essentially located in the central area of Norway's second largest city. Gullsteinen, a large hill located south of the summit of Løvstakken, is also part of the mountain massif and borders the protected forest area of Langeskogen.
17. Mon Plaisir
Mon Plaisir is a gazebo pavilion in Fjellveien, north of Mulelven, in Ladegården in Bergen. As part of the park for the Christinegård pleasure centre, the pavilion was built by Michael D. Prahl around 1836. The wooden building is shaped like a small Roman temple with Ionic columns. The French text "MON PLAISIR" is painted on the frieze of the temple front and means my joy.
18. Solheim kapell
Solheim Chapel is located at Solheim Cemetery at Solheim in the Årstad district of Bergen. The chapel was built in 1919 according to drawings by architect Sigurd Lunde and consecrated on 13 October 1920.
19. Sjømannsmonumentet
The Seamen's Monument is a monument at Torgallmenningen in Bergen, designed by the artist Dyre Vaa in the years 1939—45 and unveiled in 1950. The monument consists of twelve male figures and reliefs in two heights, cast in bronze, mounted on a large square plinth in granite. The monument was financed with collected funds, and has since been supplemented with a water surface at the foot of the pedestal.
20. Trikkehallen
Trikkehallen is located at Thormøhlensgate 23 in the Møhlenpris district of Bergen. The tram hall is owned by the City of Bergen and is currently used by the Bergen Museum of Science and Technology. The facility consists of a number of different buildings. The main buildings are the tram hall, the garage building and the omnibus workshop. The nearest neighbor is Trikkebyen, which is housing for the tramway officials.
21. Snorremonumentet
The Snorrem monument is the names of monuments in Norway and Iceland raised in memory of Snorre Sturlason, an Icelandic poet and chief who is best known for writing Heimskringla, a collection of sagas or stories about Norwegian kings, in the 1220s. "The Snorrhmonument" in Oslo , also referred to as "Snorre-Steinen" and "Snorre-Bautaen", was a monument at Nisseberget at Slottsparken at the end of Karl Johans gate. The monument was an eight meter high bauta in granite. It was unveiled by Gulbrand Lunde, who was Minister of Culture in Vidkun Quisling's second government, September 23, 1941 on the 700th anniversary of Snorre Sturlasson's death. The monument was removed at liberation after World War II. It is uncertain what happened to the bauta. July 20, 1947, a memorial was unveiled over Snorre on Reykholt in Iceland, the place he lived from 1206 until he was killed in 1241. The monument consists of a sculpture designed by the Norwegian sculptor Gustav Vigeland in 1938 and was intended as a gift for 700 -The annual mark for Snorre's death. In 1948, a copy of the monument was set up on the square at Mary's Church in Bergen. It was later moved to the Dreggsallmenningen at the entrance to the Bryggens Museum. Vigeland's statue of Snorre is 2.54 meters high and stands on an approximately three meter high shelf. The shelf has the inscriptions "Snorri Sturluson", "1178", "1241" and "Norwegians Reistu".
22. Bergen Offentlige Bibliotek

Bergen Public Library is a library building and public library institution in Bergen, Norway. Founded in 1872, it is the second largest public library in Norway. In addition to the main building in Bergen's city centre, Bergen Public Library operates nine branch offices and the library service in Bergen's two prisons.
23. St. Jørgen hospitalkirke

St George's Church, Bergen is a historic church of the Church of Norway in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. This is also the site of the Leprosy Museum. Although it is no longer regularly used, it is one of the churches in the Bergen domprosti parish which is part of the Bergen domprosti (arch-deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The green, wooden church was built in a cruciform design in 1706 using plans drawn up by an unknown architect. The church seats about 125 people.
24. Galleriet
Galleriet is a shopping mall at Torgallmenningen in central Bergen. The centre opened on 12 November 1988 and is one of Bergen city centre's largest shopping centres. The center has 70 stores in most industries, spread over 7 floors. In 2018, the centre underwent extensive rehabilitation.
25. Social Science Library
The University Library in Bergen was officially established in 1948, but is a continuation of the Bergen Museum's library, which was founded at the same time as the museum itself by Diocesan Governor Wilhelm Frimann Koren Christie in 1825. The University Library is a public scientific library. The library is part of the overall academic and educational offer at the University of Bergen.
Wikipedia: Universitetsbiblioteket i Bergen (NO), Website En
26. Norges Fiskerimuseum
The Norwegian Museum of Fisheries is a museum in Bergen for fisheries, hunting and aquaculture, founded in 1880. Until 1993, the museum was called the Fisheries Museum in Bergen and after the museum reform in 2005 became part of Museum Vest.
27. Theta museum
The Theta Museum is a museum in Bergen, Norway. It is a one-room museum in a room that was used by the Norwegian resistance group known as the Theta group to send radio messages to England under the Nazi German occupation during World War II. The room was opened to the public in 1982, and is the smallest museum in Norway.
28. Nordnesparken
The Nordnes Park is a public park in the municipality of Bergen in Vestland county, Norway. The park is located near the centre of the city of Bergen on the northwestern end of the Nordnes peninsula. It was established in 1888-1898 after an initiative from Edvard G. Johannessen in Det nyttige Selskab. The park covers about 32.7 decares of land.
29. St. Jakob kirke
Saint James's Church is a special parish church in Bergen municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located in the Nygård area of the city of Bergen. The church is part of Bergen Cathedral parish in the Bergen domprosti (arch-deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The white, plastered brick church was built in a long church design in 1921 using plans drawn up by the architect Daniel Muri. The church, which seats about 550 people, was consecrated on 5 May 1921.
30. Gestapo Museum
The Gestapo Museum is a digital experience center in Bergen at the address Veiten 3. The entrance to the Gestapo Museum is located in Chr. Michelsens gate 10. The museum itself is located on the building's 4th floor. An elevator for the disabled is located at the entrance from Veiten 3. The museum is owned and operated by the Lenken Foundation.
31. Landås kirke
Landås Church is a parish church of the Church of Norway in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located in the Landås neighborhood in the Årstad borough of the city of Bergen. It is the church for the Landås parish which is part of the Bergensdalen prosti (deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The white, concrete church was built in a fan-shaped design with a very modern style in 1966 using plans drawn up by the architect Ola Kielland-Lund. The church seats about 600 people.
32. Skur 11
Skur 11 is an 8 x 30 metre building at Bryggen in Bergen. The shed was built in 1905-1906 by the Bergen Port Authority according to drawings by Johs. Meyer. The shed has a simple steel structure and is covered with green wall panels. The building has eight granite columns that were originally adorned with wrought iron décor.
33. Christiestøtten
The Christie Pillar is a statue of the President of the Storting and Eidsvoll man Wilhelm Frimann Koren Christie (1778–1849) on the Museum Square in front of the Bergen Museum's natural history collections in Bergen. From here, he looks out over Christie's street, the street that bears his name through the city center, and reminds us to follow the constitution. The cloak hanging over the shoulder, the boots and the scroll are reminiscent of statues from Roman times, and are an expression of the artist Christopher Borch's ambition to highlight the historical significance of Christie's efforts for Norway.
34. Jesus Lever-steinen
The Jesus Lever Stone is a stone with the inscription "JESUS LEVER", along the path on the way up Løvstakken. The carving was made by master mason Alfred Westerlid, an active member of Bergen Indremisjon, sometime in the early 1900s. The stone is also called the Yellow Stone.
35. Permanenten
The West Norway Museum of Decorative Art, also referred to as KODE 1, is located in Bergen, Norway. It was established in 1887 at the initiative of Johan Bøgh. In 1896 the museum moved into a permanent exhibition building, a Renaissance Revival structure designed by Henry Bucher (1864–1944). The building caught fire during the 1916 Bergen fire but was saved.
Wikipedia: West Norway Museum of Decorative Art (EN), Website, Mapillary
36. Fridalen kirke
Fridalen Church is a parish church of the Church of Norway in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located in the Fridalen neighborhood in the borough of Årstad in the city of Bergen. It is the church for the Fridalen parish which is part of the Bergensdalen prosti (deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The white, stone church was built in a rectangular style in 1937 using designs by the architect Peter Andersen. The church seats about 450 people.
37. Urdihuset

The Urdi House is a manor house in the Gyldenpris neighborhood just outside downtown Bergen, Norway. It is located at Michael Krohn Street no. 62. The house is a prime example of late Empire style architecture. The architect that designed the house is uncertain, but it has been attributed to the town surveyor Ole Peter Riis Høegh, who was active in the town between 1834 and 1848. The Urdi House received protected status in 1927.
38. St. Markus kirke
St. Mark's Church is a parish church of the Church of Norway in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located in the Løvstakksiden neighborhood in the borough of Årstad in the city of Bergen. It is one of the two churches for the Løvstakksiden parish which is part of the Bergensdalen prosti (deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The white, plastered brick church was built in a long church design and in an art deco style in 1939 using plans drawn up by the architects Sverre Losnedahl and Nicolay Brøndmo. The church seats about 650 people.
39. The blue stone
The Blue Stone is a monument in the city of Bergen, Norway. The stone is nine meters long, and made of Brazilian sodalite. It is resting on a stone block, which gives it a characteristic inclination towards the northeast. The entire sculpture is placed on a larger foundation along with a smaller gray square stone sculpture that appears as a cover to an opening at the end of the foundation. It is considered a typical meeting point for the locals. In 2007 the rock was covered with pink plastic as a part of a marketing stunt, and after the 2011 Norway attacks it was used as a memorial site and covered with flowers.
40. Årstad kirke
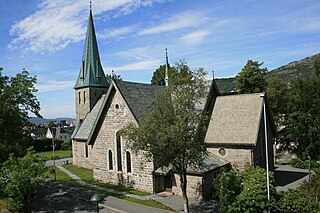
Årstad Church is a parish church of the Church of Norway in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located in the Årstad neighborhood in the city of Bergen. It is the church for the Årstad parish which is part of the Bergensdalen prosti (deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The large, stone church was built in a cruciform design and a Neo-Gothic style in 1890 using plans drawn up by the architect Christian Christie. The church seats about 560 people.
41. Storetveit kirke
Storetveit Church is a parish church of the Church of Norway in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located in the Fjøsanger neighborhood in Årstad borough in the city of Bergen. It is the church for the Storetveit parish which is part of the Bergensdalen prosti (deanery) in the Diocese of Bjørgvin. The large, stone church was built in a long church design in 1930 using plans drawn up by the architect Ole Landmark. The church seats about 600 people.
42. Bergen Technical Museum
Bergen Technical Museum is a technical museum located at Møhlenpris in Bergen, Norway. It is owned and run by various local membership groups with each their own specialized collections, which is collectively displayed in an old tram depot.
43. Nykirken
Nykirken in Bergen is a cruciform church from 1758–1763 on Nykirkeallmenningen at Nordnes in Bergen. It is the youngest of Bergen's old parish churches and was a parish church for the residents of Stranden. The church was first erected in 1621. After the great fire in 1756, the rebuilt Nykirken became both larger and different from the simple, rectangular building from 1621.
Share
How likely are you to recommend us?
Disclaimer Please be aware of your surroundings and do not enter private property. We are not liable for any damages that occur during the tours.