Self-guided Sightseeing Tour #1 in Pompei, Italy
Legend
Tour Facts
6.5 km
116 m
Experience Pompei in Italy in a whole new way with our free self-guided sightseeing tour. This site not only offers you practical information and insider tips, but also a rich variety of activities and sights you shouldn't miss. Whether you love art and culture, want to explore historical sites or simply want to experience the vibrant atmosphere of a lively city - you'll find everything you need for your personal adventure here.
Individual Sights in PompeiSight 1: Lupanar (brothel)
.jpg)
The Lupanar is the ruined building of an ancient Roman brothel in the city of Pompeii. It is of particular interest for the erotic paintings on its walls, and is also known as the Lupanare Grande or the "Purpose-Built Brothel" in the Roman colony. Pompeii was closely associated with Venus, the ancient Roman goddess of love, sex, and fertility, and therefore a mythological figure closely tied to prostitution.
Sight 2: Terme Stabiane
The Stabian Baths are an ancient Roman bathing complex in Pompeii, Italy, the oldest and the largest of the 5 public baths in the city. Their original construction dates back to ca. 125 BC, making them one of the oldest bathing complexes known from the ancient world. They were remodelled and enlarged many times up to the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD.
Sight 3: Pompeii
The archaeological excavations of Pompeii have returned the remains of the ancient city of Pompeii, near the hill of Civita, at the gates of modern Pompeii, buried under a blanket of ashes and lapilli during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79, together with Herculaneum, Stabia and Oplontis.
Sight 4: Domus Lucreti
The house of Marcus Lucretius is a house from Roman times, buried during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: also called the house of the Musicians, it owes its name to that of the alleged owner, Marcus Lucretius.
Sight 5: Regio IX
The list includes the monuments present in Regio IX of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
Sight 6: Casa dei Gladiatori (V.5.3)
The Gladiators' house is located in Pompeii.
Sight 7: Regio V
The list includes the monuments present in Regio V of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
Sight 8: House of the Silver Wedding
The House of the Silver Wedding is the name given to the archaeological remains of a Roman house in Pompeii, buried in the ash from the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. The house was excavated in 1893 and was named after the silver wedding anniversary of Umberto I of Italy and Margherita of Savoy, which took place in that year.
Sight 9: Casa di Cecilio Giocondo
The house of Lucius Caecilius Giocondo is a house from the Roman era, buried during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii.
Sight 10: House of the Ara Maxima
The house of the Ara Massima is a house from Roman times, buried during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: it is also called the house of Narcissus or the house of Pinarius.
Sight 11: Castellum aquae
The Castellum Aquae is a building from the Roman era, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: its function was to collect drinking water and distribute it to the city water network.
Sight 12: Regio IV
The list includes the monuments present in Regio IV of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
Sight 13: Palestra Grande
The large gym, located in Regio II, is a Roman gym, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius of 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: its name derives from the fact that it was the greatest gymnastic system of the city.
Sight 14: Regio II
The list includes the monuments present in Regio II of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
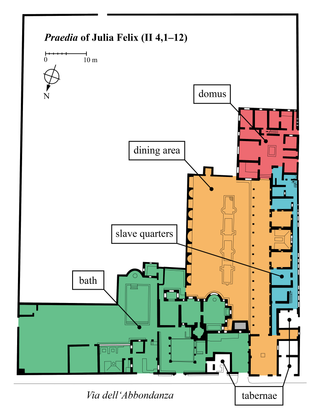
Sight 15: House of Julia Felix
The House of Julia Felix, also referred to as the praedia of Julia Felix, is a large Roman property on the Via dell'Abbondanza in the city of Pompeii. It was originally the residence of Julia Felix, who converted portions of it to apartments available for rent and other parts for public use after the major earthquake in 62 AD, a precursor to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD that destroyed Pompeii.
Sight 16: Casa di Octavius Quartione

The House of Loreius Tiburtinus is renowned for well-preserved art, mainly in wall-paintings as well as its large gardens.
Sight 17: Regio III
The list includes the monuments present in Regio III of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
Wikipedia: Regio III degli scavi archeologici di Pompei (IT)
Sight 18: Schola Armaturarum
The Schola dashboard was a meeting house in Pompeii. It was excavated by Vittorio Spinazzola in 1915. The building consisted of a hall and some rooms behind it that still came from a predecessor building when a private house was here. The Schola Kingdarum probably served as a place of assembly of a military organization shortly before the fall of the city. During the excavations, there were numerous weapons that were once housed on shelves along the walls. The wood of the shelves had already passed largely during the excavations, but holes were still seen on a wall for the shelves. The wide entrance was once blocked with a wooden grille that could be reconstructed due to plaster casts. The wood of the grid had long passed, but left a cavity that was filled with plaster during the excavations. The pillars on both sides of the entrance were painted with trophies and weapons. Wall paintings with military badges and candelabries were also found inside the hall.
Sight 19: Casa della Venere in Bikini
The house of Venus in a Bikini, also known as the house of Maximus, is a house from Roman times, buried during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii.
Sight 20: House of Pomarius Felix
The list includes the monuments present in Regio I of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
Sight 21: Casa dell'Efebo
The House of the Ephebe is a house from Roman times, buried during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: also called the house of Publius Cornelius Tegestes, from the name of the owner, it owes its name to the discovery of a statue depicting an ephebe.
Sight 22: House of the Ceii
Sight 23: Quadriportico dei Teatri
The Quadriportico dei Teatri, also called the Gladiators' Barracks, is a Roman structure, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: initially used as a foyer, it was later transformed into barracks for gladiatorial art.
Sight 24: Teatro Piccolo
The theatre area of Pompeii is located in the southwest region of the city. There are three main buildings that make up this area: the Large Theatre, the Odeon, and the Quadriporticum. These served as an entertainment and meeting centre of the city. Pompeii had two stone theatres of its own nearly two decades before the first permanent stone theatre was erected in Rome in the 50s BC.
Sight 25: Doric Temple
The Doric Temple is a Roman temple, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii. It is one of the buildings with the greatest Greek influences in the city.
Sight 26: Temple of Isis
The Temple of Isis is a Roman temple dedicated to the Egyptian goddess Isis. This small and almost intact temple was one of the first discoveries during the excavation of Pompeii in 1764. Its role as a Hellenized Egyptian temple in a Roman colony was fully confirmed with an inscription detailed by Francisco la Vega on July 20, 1765. Original paintings and sculptures can be seen at the Museo Archaeologico in Naples; the site itself remains on the Via del Tempio di Iside. In the aftermath of the temple's discovery many well-known artists and illustrators swarmed to the site.
Sight 27: Samnite Gymnasium
The Samnite Gym is a Roman gymnasium, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: its function was to host gymnastic competitions or military and political meetings.
Sight 28: Foro Triangolare
The Triangular Forum is a Roman forum, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii; The square was mainly used for equestrian races and as a place of recreation while waiting to attend the performances of the nearby theaters.
Sight 29: Regio VIII
The list includes the monuments present in Regio VIII of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
Wikipedia: Regio VIII degli scavi archeologici di Pompei (IT)
Sight 30: Edificio di Eumachia
The Building of Eumachia was a public building from Roman times, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: the building was used as a wool market or as the headquarters of the fullones guild.
Sight 31: Tempio di Vespasiano
The temple of Vespasian, also known as Aedes Genii Augusti, is a Roman temple, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: the sacred structure was dedicated to the genius of the Roman emperors.
Sight 32: Temple of Jupiter
The Temple of Jupiter, Capitolium, or Temple of the Capitoline Triad, was a temple in Roman Pompeii, at the north end of its forum. Initially dedicated to Jupiter alone, it was built in the mid-2nd century BC at the same time as the Temple of Apollo was being renovated – this was the area at which Roman influence over Pompeii increased. So Roman Jupiter superseded the Greek Apollo as the town's leading divinity. Jupiter was the ruler of the gods and the protector of Rome, where his temple was the center of Roman religion and of the cult of state.
Sight 33: Temple of Fortuna Augusta
The temple of Fortuna Augusta is a Roman temple, buried during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: it was dedicated to Emperor Augustus.
Sight 34: House of the Faun
The House of the Faun, constructed in the 2nd century BC during the Samnite period, was a grand Hellenistic palace that was framed by peristyle in Pompeii, Italy. The historical significance in this impressive estate is found in the many great pieces of art that were well preserved from the ash of the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. It is one of the most luxurious aristocratic houses from the Roman Republic, and reflects this period better than most archaeological evidence found even in Rome itself.
Sight 35: Casa VI 14, 28.33 Sog. Casa di Laocoonte
The House of Laocoön is a Roman house, buried during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: it owes its name to a cycle of paintings found in the atrium.
Sight 36: House of the Labyrinth
The House of the Labyrinth is a domus of Pompeii, largely dated to the Republican period.
Sight 37: Casa dei Dioscuri
The House of the Dioscuri is a Roman house, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: it is one of the largest and best decorated houses in the city and owes its name to a painting located at the entrance, depicting the Dioscuri Castor and Pollux, now preserved in the National Archaeological Museum of Naples.
Sight 38: Regio VI
The list includes the monuments present in Regio VI of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
Sight 39: Casa di Sallustio
The House of Sallust was an elite residence (domus) in the ancient Roman city of Pompeii and among the most sumptuous of the city.
Sight 40: Forum Baths
The Baths of the Forum, also called the Baths of Fortune, are a thermal complex from Roman times, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: they take their name from their proximity to the forum.
Sight 41: Macellum
The Macellum of Pompeii was located on the Forum and as the provision market of Pompeii was one of the focal points of the ancient city. The building was constructed in several phases. When the earthquake of 62 AD destroyed large parts of Pompeii, the Macellum was also damaged. Archeological excavations in the modern era have revealed a building that had still not been fully repaired by the time of the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD.
Sight 42: Regio VII
The list includes the monuments present in Regio VII of the archaeological excavations of Pompeii.
Wikipedia: Regio VII degli scavi archeologici di Pompei (IT)
Sight 43: Santuario dei Lari Pubblici
The sanctuary of the Public Lares is a Roman temple, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii; inside, in all likelihood, the tutelary deities of the city were worshipped.
Sight 44: Foro di Pompei
The Forum of Pompeii is a Roman forum, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii. The structure was the main square of the city and represented the political, economic and religious center in which demonstrations, commercial negotiations and debates took place; It is, of its kind, one of the best preserved of the ancient Italic cities.
Sight 45: Temple of Apollo

The Temple of Apollo, also known as the Sanctuary of Apollo, is a Roman temple built in 120 BC and dedicated to the Greek and Roman god Apollo in the ancient Roman town of Pompeii, southern Italy. The sanctuary was a public space influenced by Roman colonists to be dedicated to Greco-Roman religion and culture.
Sight 46: Basilica
The Basilica was a public building from Roman times, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: it was used both as a court and as a venue for commercial negotiations.
Sight 47: Temple of Venus
The temple of Venus is a temple from the Roman era, buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 and found following the archaeological excavations of ancient Pompeii: it was the temple where the patron deity of the city was worshipped, as well as one of the most sumptuous.
Sight 48: Terme Suburbane

The Suburban Baths are a building in Pompeii, Italy, a town in the Italian region of Campania that was buried by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, which consequently preserved it.
Share
How likely are you to recommend us?
Disclaimer Please be aware of your surroundings and do not enter private property. We are not liable for any damages that occur during the tours.
GPX-Download For navigation apps and GPS devices you can download the tour as a GPX file.



.jpg)